New possibilities for efficient and sustainable farming

IoT technology offers a powerful tool for precision agriculture, allowing farmers to gather and analyze data on a wide range of factors in real-time. Data-driven decision-making can help farmers optimize their operations, increase yields, and reduce waste and resource consumption.
The agriculture industry is increasingly adopting IoT solutions, including Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) sensors for cost-effective monitoring. However, the usage of BLE sensors has been limited to indoor environments with Wi-Fi or mobile gateways.
IoT Mill BLE Gateway enables the implementation of a battery-operated BLE to NB-IoT gateway in agriculture, overcoming this limitation and enabling BLE sensor deployment in remote areas.
So what is the problem?
BLE sensors rely on indoor settings with power-connected gateways, which hampers their deployment in remote locations lacking such infrastructure.

Solution
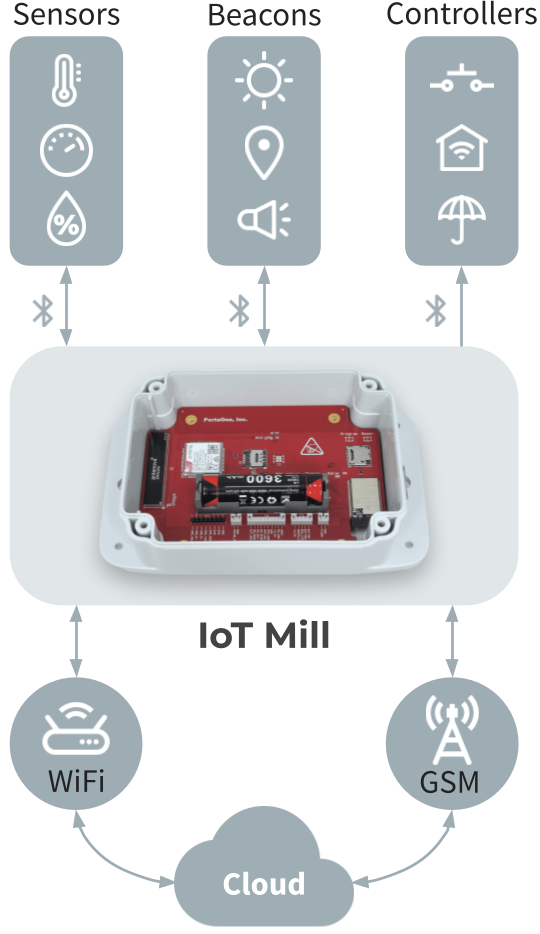
The IoT Mill BLE Gateway opens new possibilities for agriculture monitoring. It enables BLE sensors to operate in any location, transforming the way we monitor crops and soil. Acting as an intermediary, this battery-operated gateway collects data from BLE sensors that can be used for:
- Soil monitoring: Soil sensors can be used to monitor moisture levels, temperature, and nutrient content in the soil, helping farmers to optimize irrigation and fertilizer application. This can help farmers make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and irrigation.
- Crop monitoring: Sensor networks can be used to monitor the growth and health of crops, providing real-time data on factors such as photosynthesis, leaf area, and yield potential.
- Pest detection: Sensors can be used to detect the presence of pests, such as insects or rodents, in the field. This can help farmers take proactive measures to prevent crop damage.
- Livestock monitoring: Sensor networks can be used to monitor the health and behavior of livestock, providing real-time data on factors such as body temperature, heart rate, and feeding patterns.
- Water management: Sensor networks can be used to monitor water usage, providing real-time data on factors such as water flow, quality, and temperature. This can help farmers optimize irrigation and conserve water resources.
Maximize your cost savings with the IoT Mill BLE Gateway.
By minimizing the number of required NB-IoT connections, you can significantly reduce your expenses. Connect multiple BLE sensors to a single gateway, eliminating the need for additional hardware and optimizing your investment. Moreover, the use of smaller battery capacities for BLE sensors not only saves costs but also ensures efficient power utilization.
Battery life and energy optimization
The gateway offers an additional energy-saving option by implementing a data collection and upload strategy. BLE data can be collected frequently, such as at one-minute intervals, and stored within the gateway. However, the upload to the NB-IoT network can occur less frequently, such as once a day. This strategy optimizes battery life for both the BLE sensors and the gateway, reducing energy consumption and enhancing overall efficiency.

Conclusion
The implementation of a battery-operated BLE to NB-IoT gateway in agriculture facilitates the deployment of BLE sensors in remote areas. It brings cost savings, extends sensor battery life, and offers an energy optimization strategy through data collection and upload intervals. By enabling data-driven decision-making, this solution empowers farmers to improve productivity and resource management. The BLE to NB-IoT gateway opens up new possibilities for efficient and sustainable agriculture practices.



